Dr Srikanta K. Panigrahi
Dr Srikanta K. Panigrahi
Director General and Distinguished Research Fellow, IISD
Indian Policy Maker and Technocrat
Lightening kills more people than cyclones in India, says the Earth Networks India Lightening Report, 2019 and it could increase as much as 12% with every 1 degree increase in Global Warming. It’s not just the northern lights that glow in the Arctic. Lightning has been striking the region more often in the past decade as the climate gets warmer, Ms Sofia Moutinho of Science News reports on 31st March 2021. The number of summertime bolts detected in latitudes higher than 65oN (above Alaska) has increased more than six times, from about 35,000 in 2010 to about 240,000 in 2020, a study in Geophysical Research Letters concludes. The spike follows rising temperatures in the region, and scientists think the warmer climate could be fuelling more thunderstorms, based on the analysis and empirical evidence, they are getting from their scientific research.
Earth Networks India Lightening Report further reports in India the peak lightening season are from June 2 September to September each year. Lightening effects are more pronounced in Eastern and North Eastern States like Jharkhand, Bihar, West Bengal, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Meghalaya, Manipur, Mizoram and Tripura etc. Although Odisha is reported to have maximum number of lightening events , but West Bengal has the highest lightening intensity.
Please find below a news item, as reported by Economics Times, on 25 June 2020; death 83 Persons died in Bihar, due to thunderstorms, in 10 district in a single day. During mansoon, particularly hundreds of people die in Eastern and North Indian States in the month of June, each year.
83 killed in Bihar due to lightning and thunderstorms in single day
Times Now | 25 Jun 2020, 08:45 PM IST
At least 83 people died due to thunderstorms in Bihar in the last 24 hours, according to Chief Minister’s Office. Bihar Chief Minister Nitish Kumar announced Rs 4 lakhs each for the families of deceased. Thirteen people died in Gopalganj, 8 each in Madhubani and Nawada, 6 each in Baghalpur and Siwan, 5 each in Darbhanga, Banka, East Champaran and 3 each in Khagaria and Aurangabad.
In addition, India Climate Dialogue Reports lightening or thunder strikes, mostly kills the farmers, while working in their agricultural fields. The reason could be the warnings don’t reach hyper-local levels. Another fact could taking shelter, under tree is very unsafe. More, using wired equipment can also enhance the life risk of anyone, during lightening. Battery operated devices, are comparatively safe, and One should not also touch any metallic objects, which normally conducts electricity.
Another option could be Ours homes and indoors should be well insulated, so that lightening cannot harm conduct heat, electricity, in addition, there should be sufficient insulating arrangements at the construction stage must be incorporated houses and especially in indoors, which should be able to prevent lightening, hence the lightening-proof construction techniques must be adopted, at least to prevent lightening of small and medium range of lightening – as one of the short term measures, in addition to adopting stronger Climate Actions (as per UN SDG 13) as a long term measure.
What Causes a Thunderstorm ?
All thunderstorms need the same ingredients: moisture, unstable air and lift. Moisture usually comes from oceans. Unstable air forms when warm, moist air is near the ground and cold, dry air is above. Lift comes from differences in air density. It pushes unstable air upward, creating a tall thunderstorm cloud. The unstable air is caused by the Climate Change Phenomenon.
What Causes a Cloudburst ? How it happens ? How it impacts ?
Cloudburst, a sudden, very heavy rainfall, usually local in nature and of brief duration. Most so-called cloudbursts occur in connection with thunderstorms. In these storms there are violent rushes of air, which at times prevent the condensing raindrops from falling to the ground.
Cloudburst is an extreme amount of precipitation in a short period of time, sometimes accompanied by hail and thunder, which is capable of creating flood conditions. Cloudbursts can quickly dump large amounts of water, e.g. 25 mm of precipitation corresponds to 25,000 metric tons per square kilometre.
A cloudburst is a sudden aggressive downpour within the radius of a couple of kilometres. Though, cloudbursts usually do not last for more than a few minutes, they are capable of flooding the entire area. Rainfall from a cloudburst is usually equal to or greater than 100 mm per hour.
Cloudburst kills. Above, in Economic Times News, We have seen – How 83 people have died in Bihar because of Thunderstorms on 25th June 2020. In addition, Economic Times has also reported, On August 15, 1997, 115 people were killed when a cloudburst occurred and trail of death was all that was left behind in Chirgaon in Shimla district, Himachal Pradesh. Also Find a video on the “Cloudburst in Uttarakhand’s Chamoli District” – on the right hand side margin. It is well known that in Uttarakhand Cloudbursts kill people and sometimes burst the himalayan glaciers at the upper stream of the rivers causing massive floods in the state.
Climate Change is triggering Lightning, Thunderstorms and Cloudbursts today. Hence, We must come forward to engage ourselves in stronger possible Climate Actions, and reset our relationship with nature.
The Author is a Leading Indian Sustainability Thought Leader and Director General at Indian Institute of Sustainable Development (IISD), New Delhi and deeply engaged in Climate Action Leadership Initiatives of UNFCCC, UNEP and Government of India.

Thunderstorms in Delhi, UP, Rajasthan, Punjab and J&K - Economic Times
What Causes a Thunderstorm ?
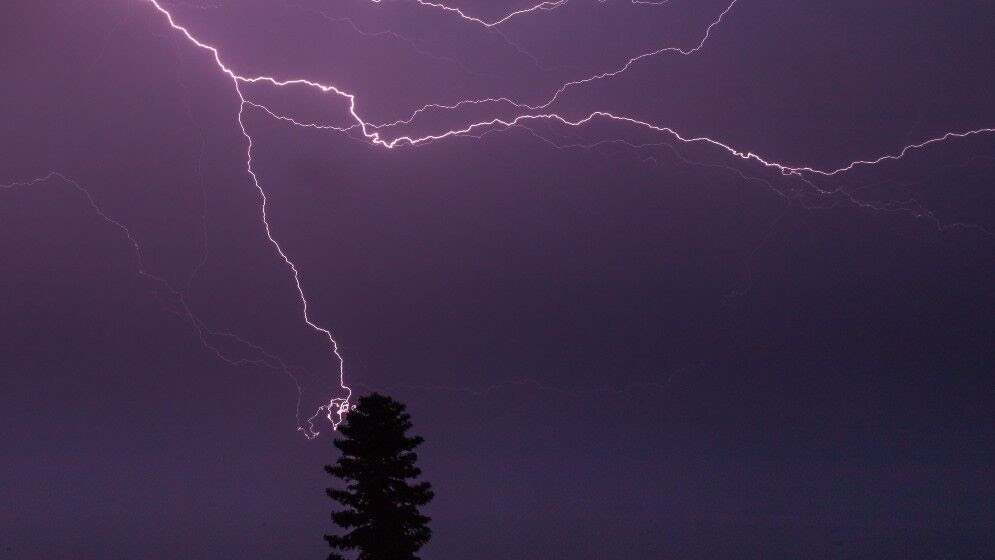

Increased Lightning in Artics, due to Climate Change Impacts - Science News Reports
Source : National Geographic Video on Thunderstorms

Lightning with a Thunderstorm
Source : Down to Earth, CSE
Cloudburst in Uttarakand's Chamoli district

Lightning, Thunderstorm with a Cloud Burst